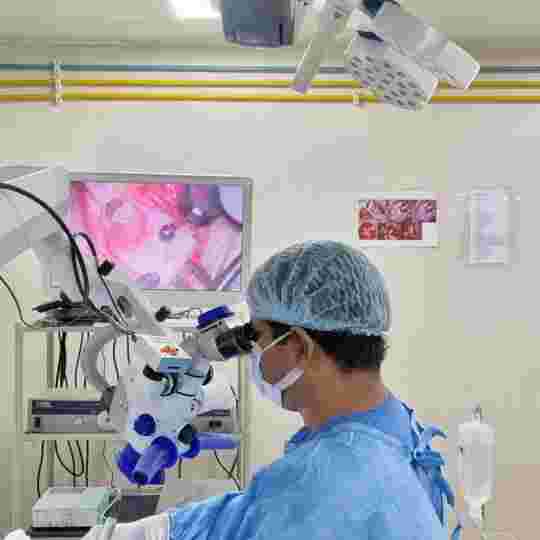
Ear Perforation
What is an ear drum?
The eardrum (also called the tympanic membrane) is a thin skin-like structure in the ear. It lies between the outer (external) ear and the middle ear.
The ear is divided into three parts – the outer, middle and inner ear. Sound waves come into the outer ear and hit the eardrum, causing the eardrum to vibrate.
Behind the eardrum are three tiny bones (ossicles). The vibrations pass from the eardrum to these middle ear bones. The bones then transmit the vibrations to the cochlea in the inner ear. The cochlea converts the vibrations to sound signals which are sent down a nerve to the brain, which we ‘hear’.
The middle ear behind the eardrum is normally filled with air. The middle ear is connected to the back of the nose by the Eustachian tube. This allows air in and out of the middle ear.
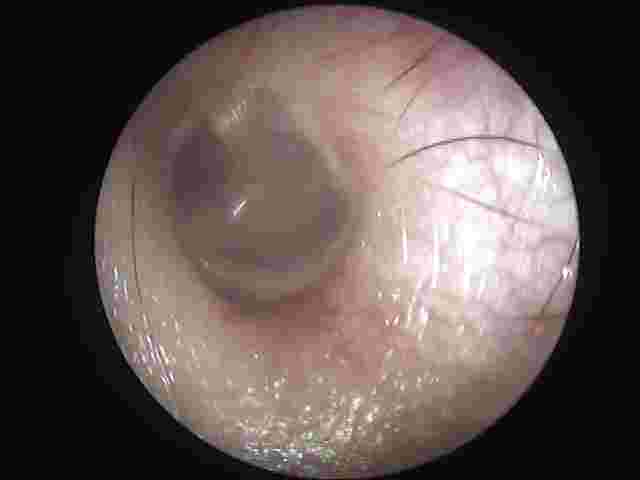
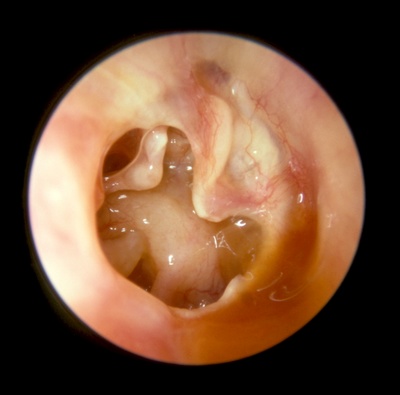
Eardrum perforation
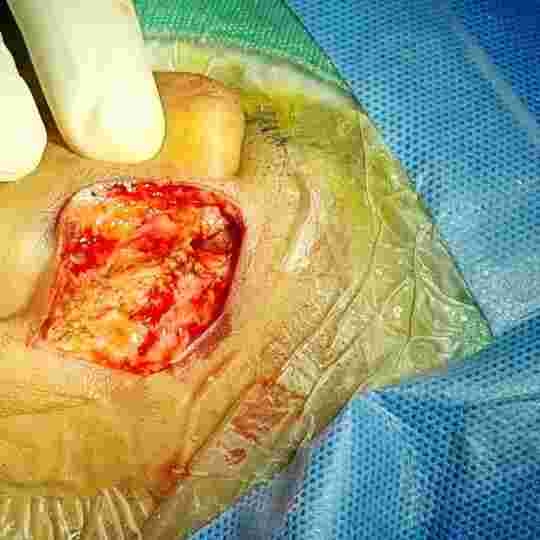
A hole or rupture in the eardrum, a thin membrane that separates the ear canal and the middle ear, is called a perforated eardrum. A perforated eardrum is a hole or tear that has developed in the eardrum. It can affect hearing. The extent of hearing loss can vary greatly –based on duration of disease, status of auditory nerve and integrity of middle ear ossicular bones.
With a perforation, you are at greater risk of developing an ear infection. This is because the eardrum normally acts as a barrier to bacteria and other germs that may get into the middle ear.
Initial stages of ear disease is limited to defect in tympanic membrane. Disease progression will lead to erosion and infection of mastoid bone (bone which is present behind your ear) and erosion of middle ear ossicles.
Tympanoplasty is a procedure of ear drum and middle ear hearing bones(ossicles) repair
Tympanoplasty with mastiodectomy means removal of disease from mastoid bone along with tympanoplasty procedure.
There are 2 types of mastoidectomy procedures
- Intact canal wall\ cortical mastoidectomy: this procedure takes 1-1.5 month to heal
- Canal wall down \ modified radical mastoidectomy: this is a more radical procedure in which your ear canal and mastoid cavity are made into a single cavity. Hearing may not be as good as in cortical cavity. This procedure is resorted in advanced diseases only. Healing in these cases takes 1-3 months for epithelisation. Post MRM patient needs to meet up regularly with ENTs every six months for regular ear cleaning/toileting.
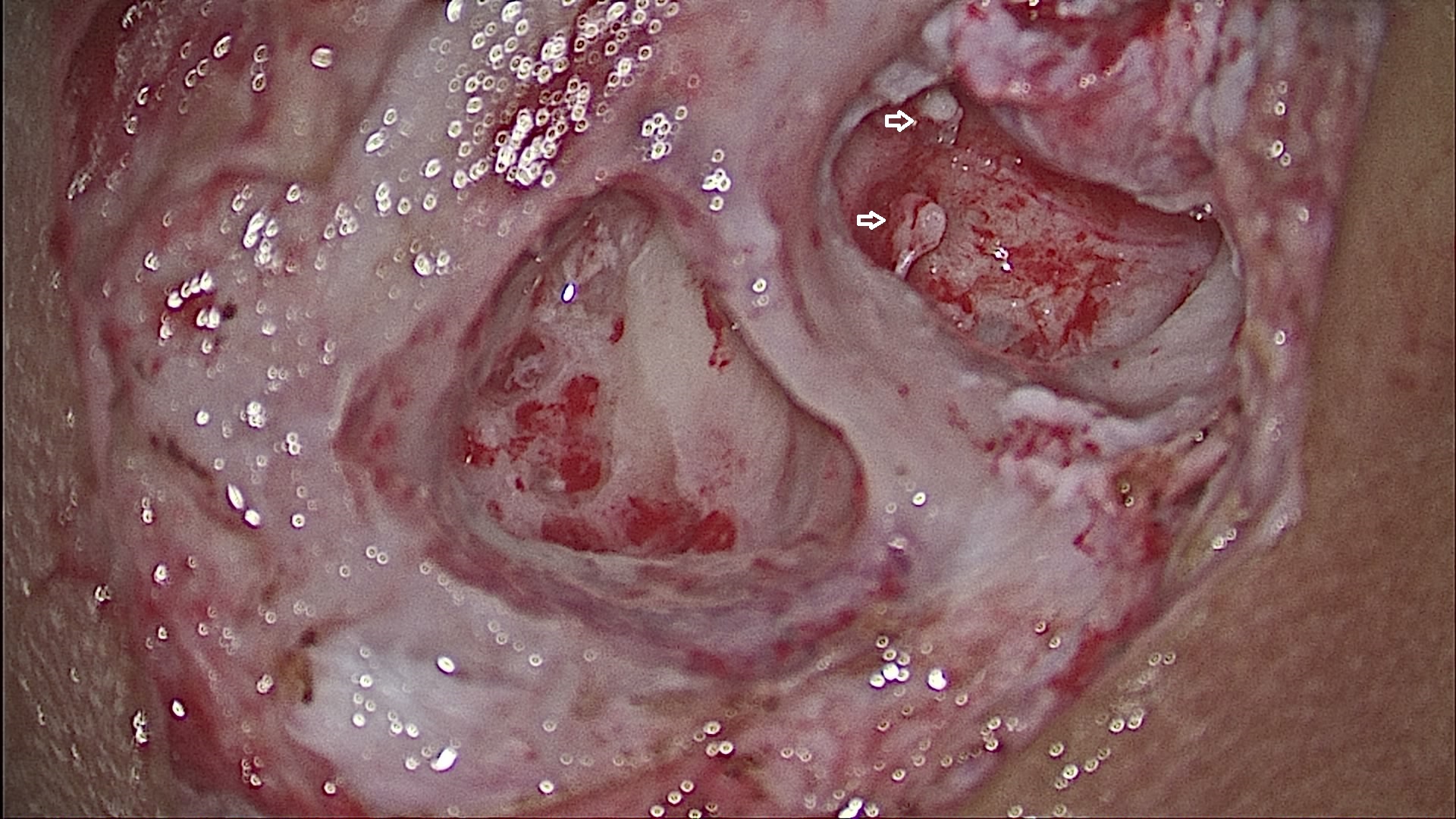
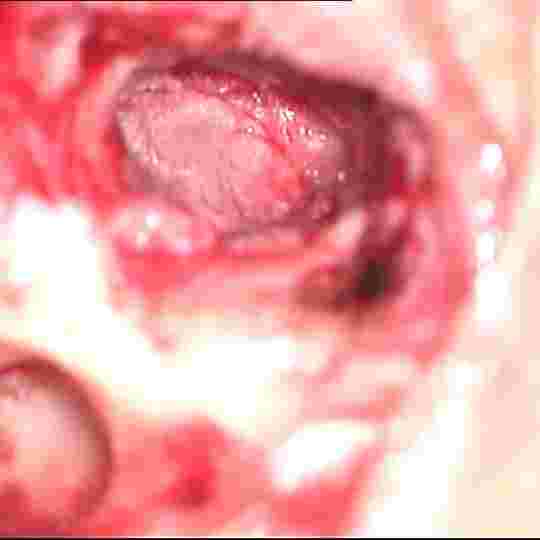
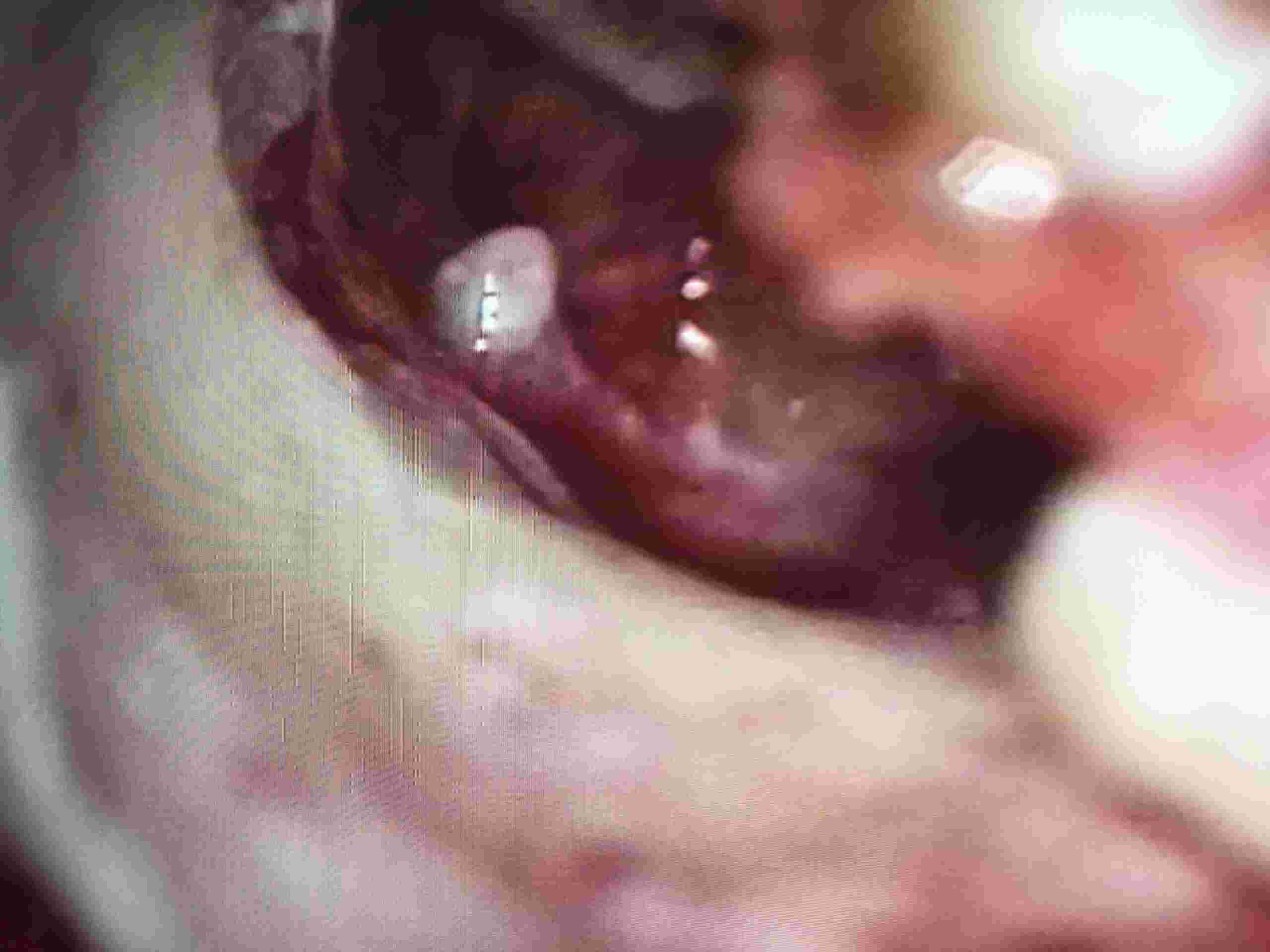
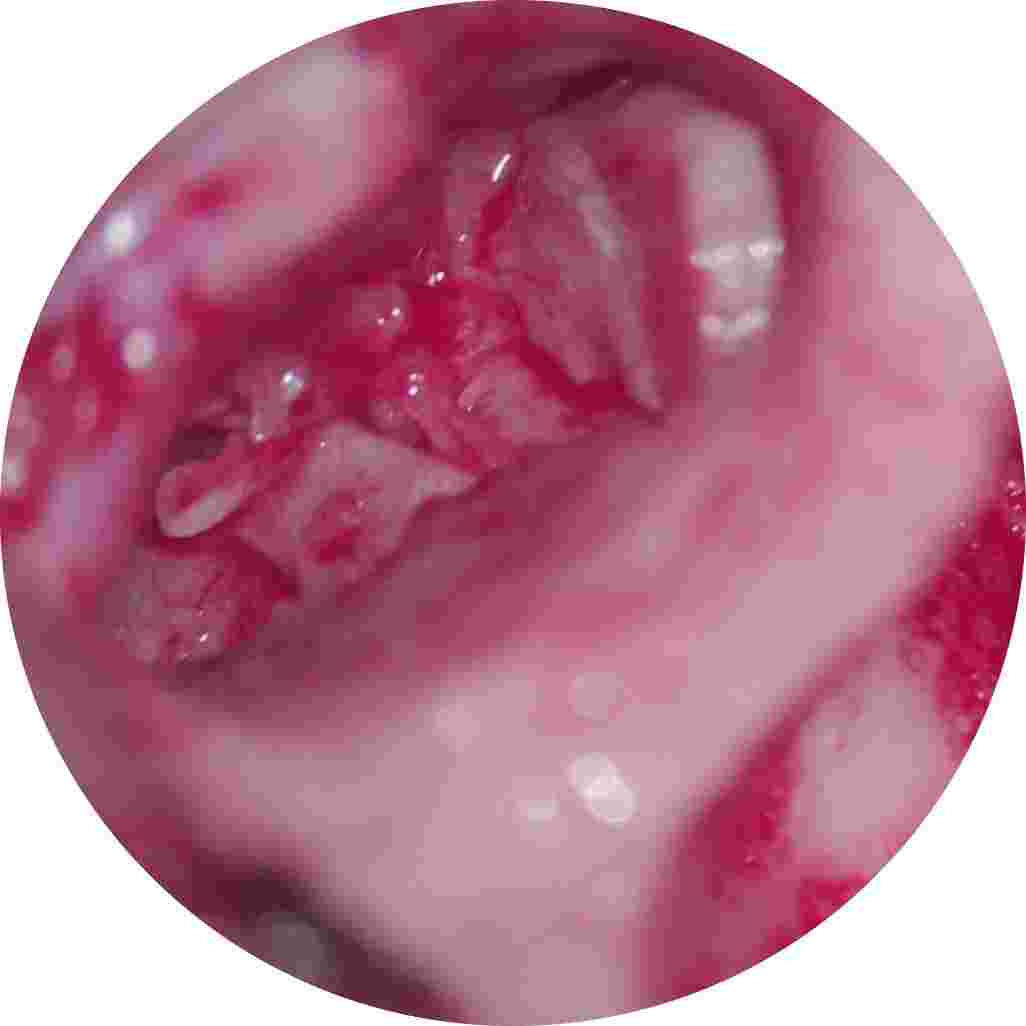
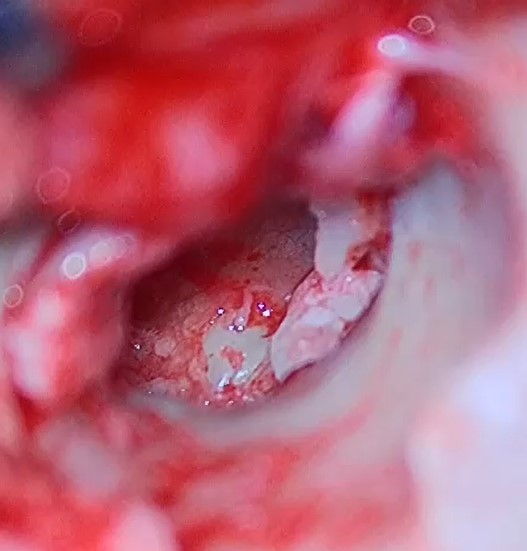
White arrows showing 1 and 3 ossicle, middle ossicle incus is missing
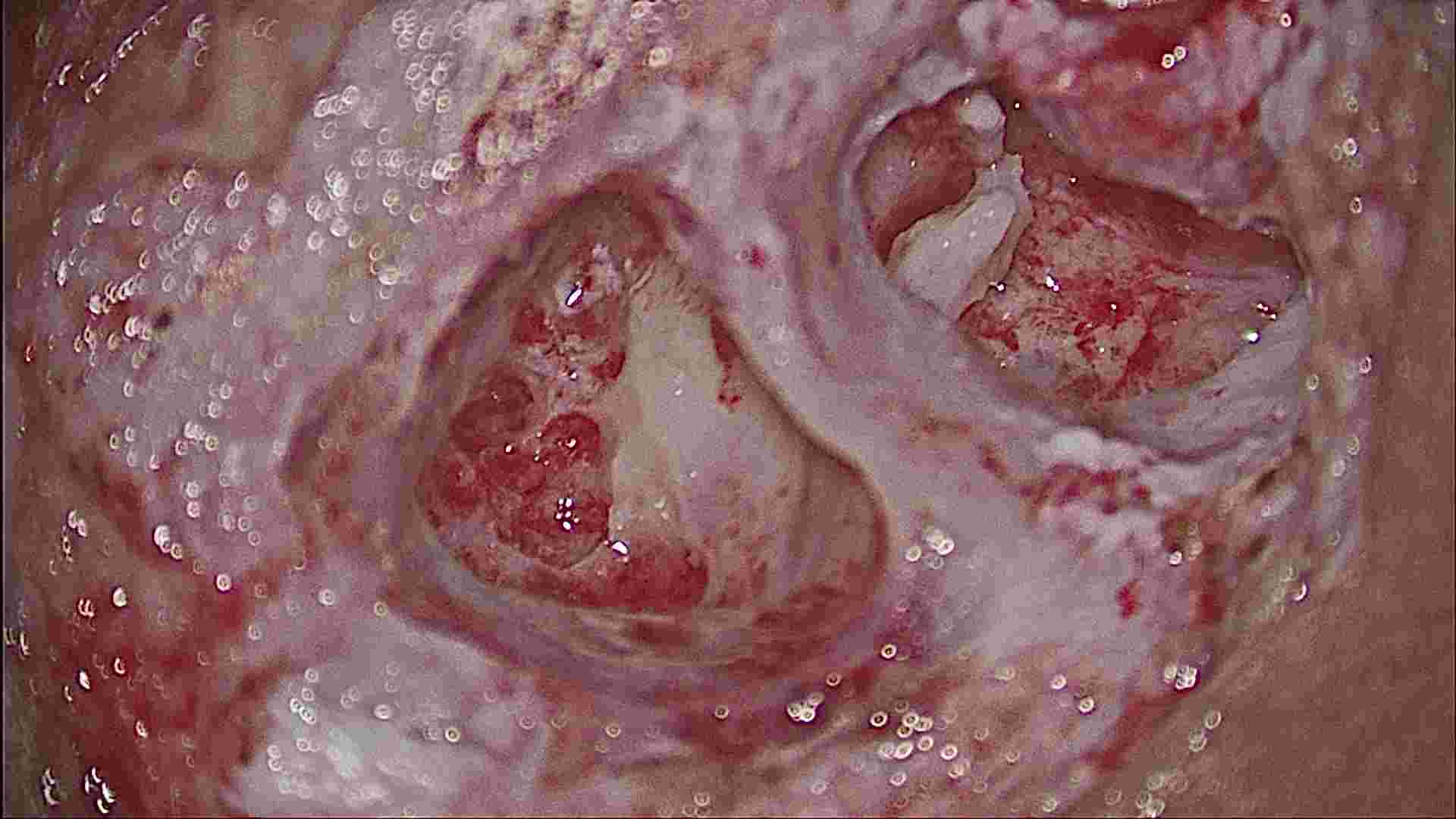
eroded middle ossicle refashioned and used to bridge gap between 1 and 3 ossicle
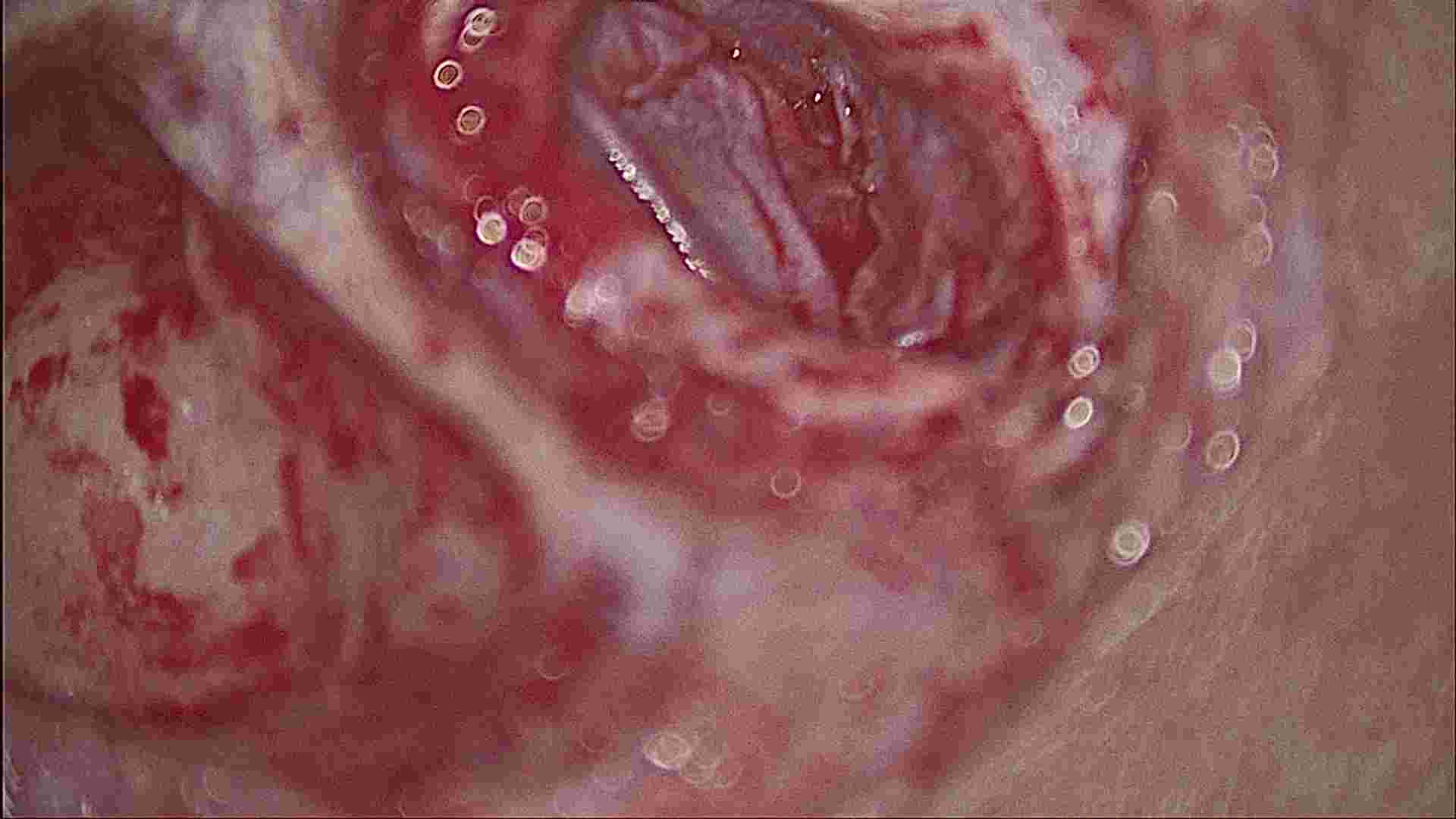
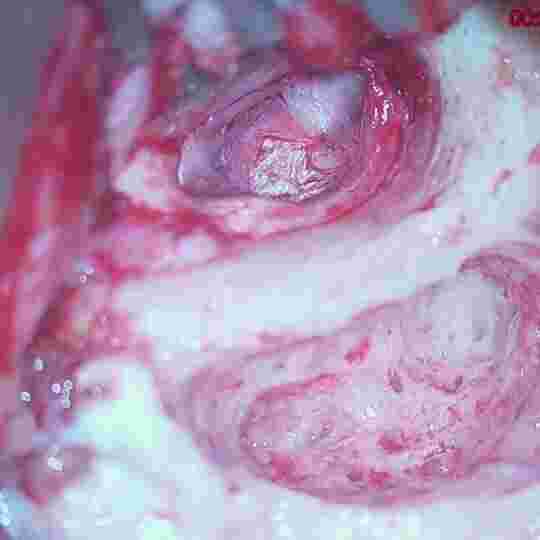
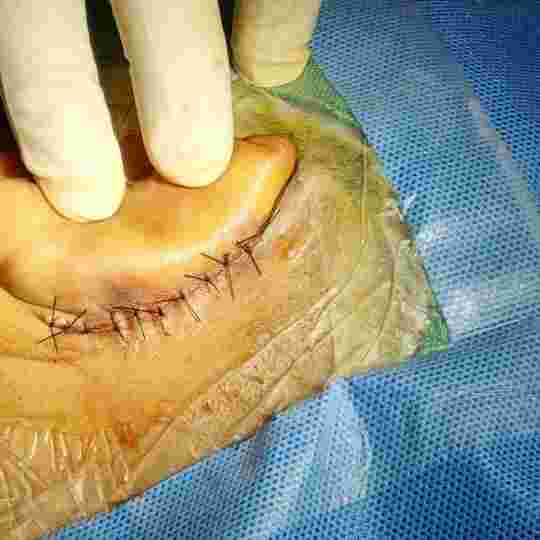
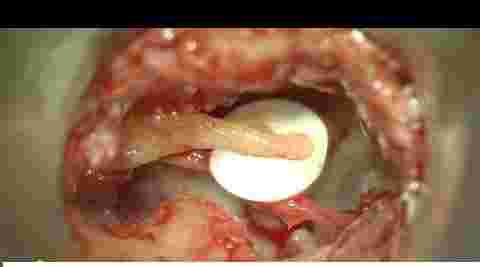
Image of reconstructed ear drum
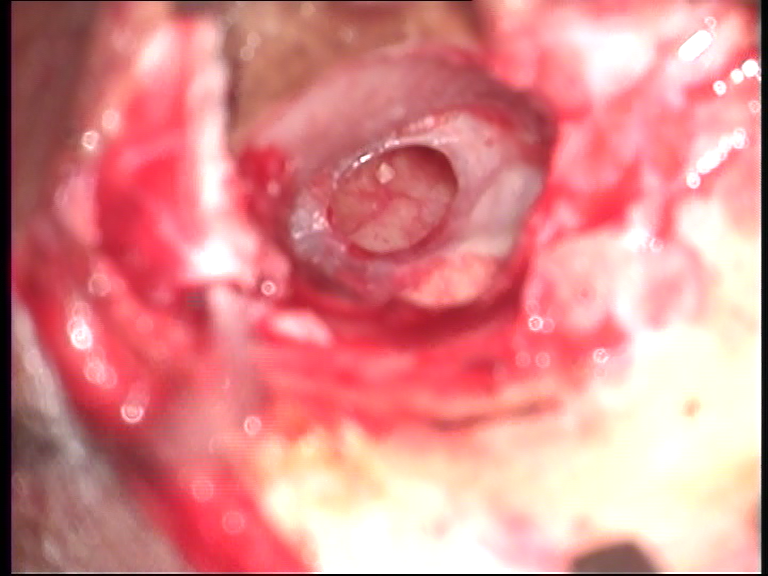

Above are Photos of reconstructed ear drum
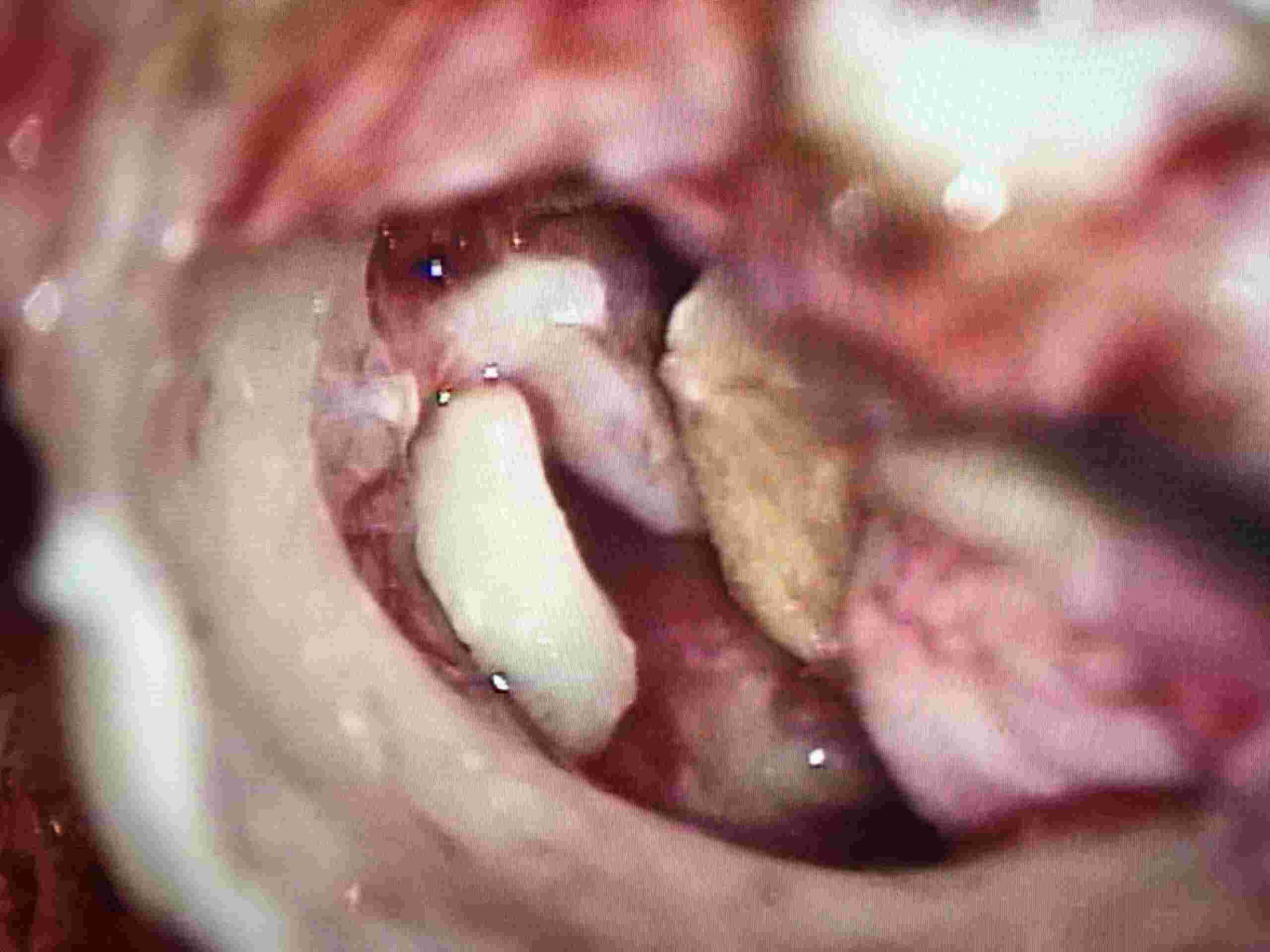
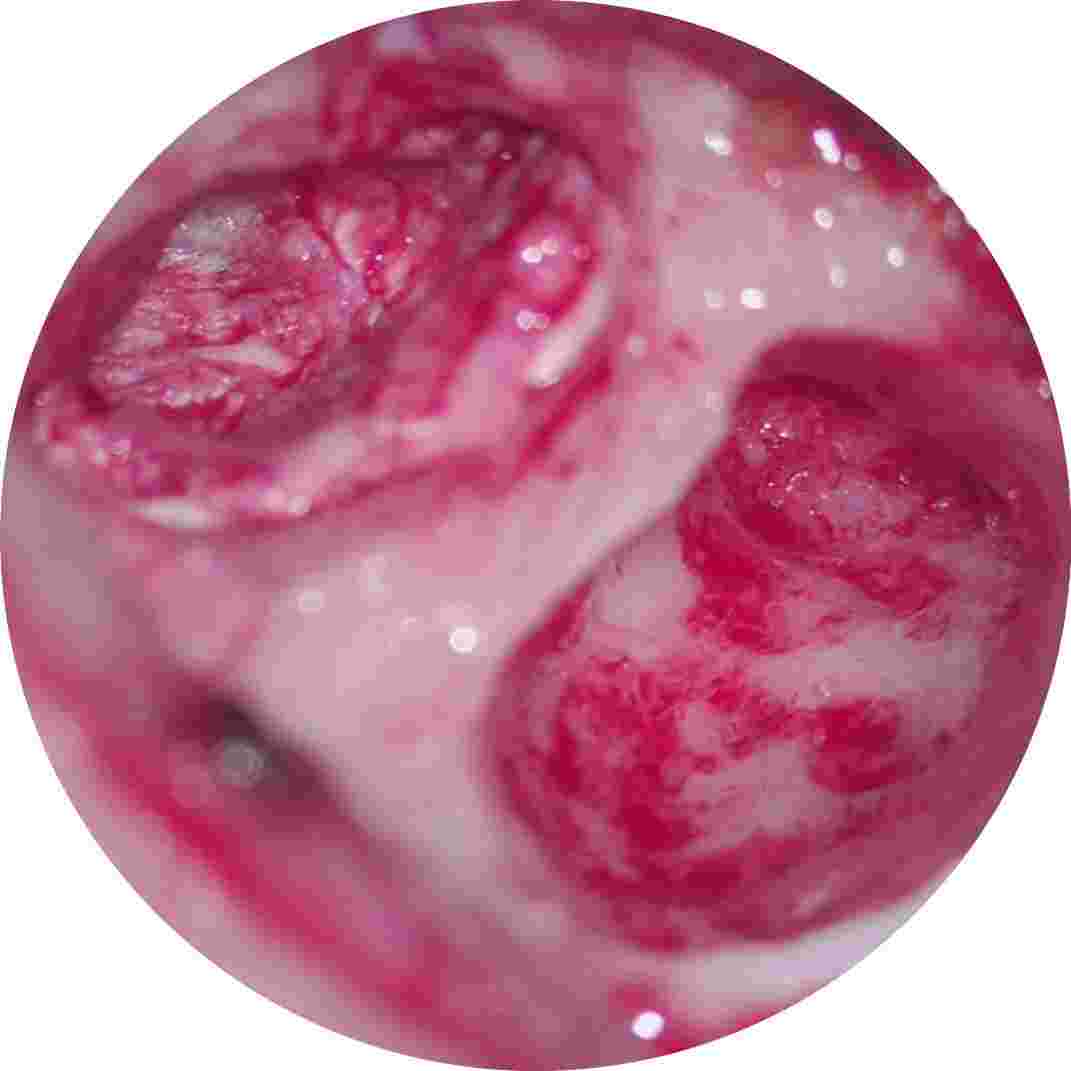
Middle ossicles reconstructed using natural bone
partially eroded middle ear bone refashioned
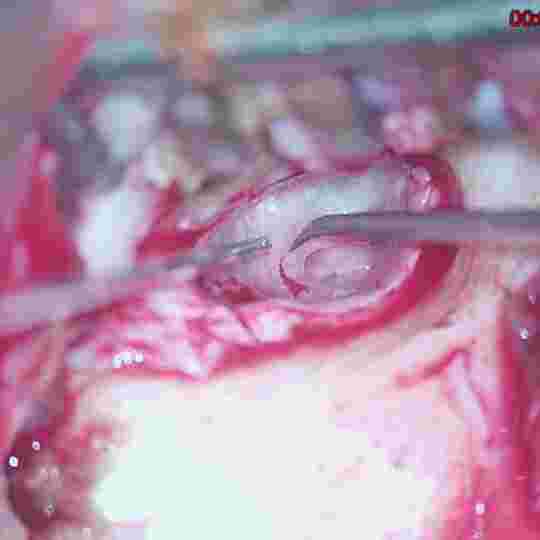
Artificial Teflon piston (PORP) used for bridging gap between first and third ossicle
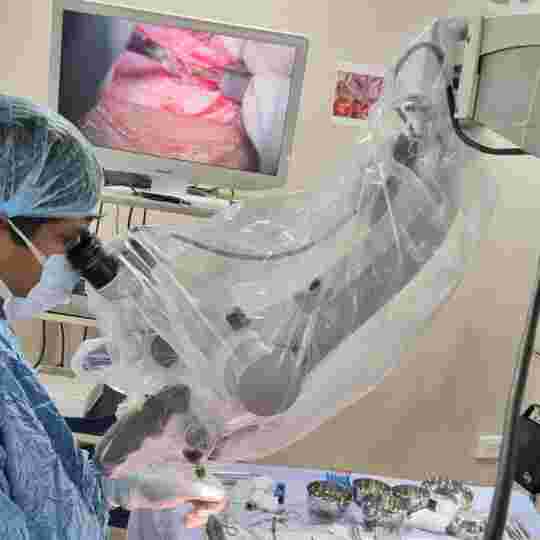
Endoscopic cartilage Boomerang ossiculoplasty
Tympanoplasty/Mastoidectomy instructions after Surgery
Two types of anaesthesia options are given to patients.
- Patients who are given local anaesthesia with IV sedation can start their diet after 3 hours of surgery and who are operated under general anaesthesia can start their diet after four hours postoperatively.
- Diet is “as tolerated” after surgery. Clear liquids will be given first and if tolerated a light food diet can be started that same day. After 6 hours after surgery the patient’s usual diet can be resumed.
- Ear may appear to protrude from the side of the head more than the opposite ear postoperatively. This is the result of post operative swelling or because of lack of hair which was removed for surgery and it should subside over a period of a few weeks.
- It may also be noticed that there is some numbness over the top of the ear or skin behind your ear after the bandages have been removed. This is the result of bruising of the sensory nerves to the ear as a result of the incision. This numbness is self-limiting and will gradually subside over a period of several months.
- Postoperative dressing should be maintained for one week. During this time dressing may get little occasional blood stains which is normal. If the bleeding becomes troublesome and is continuous, dial bayya ENT & cochlear implant centre at 0863-2225729 and get in touch with your surgeon immediately. Don’t worry it will be rectified easily.
- After the surgery is completed, the ear canal is packed with an absorbable sponge called gel foam coated with medicine. This gives the patient a feeling of ear block, occasional watery feeling or itching in the ear. This material liquefies slowly during the first month. It is wise to keep a clean piece of cotton in the ear daily in order to collect the drainage. Clean/sterile cotton plugs should be changed as needed (2-3 times per day). Cotton should be kept exteriorly not to be pushed inside the ear canal. This ear sponge helps to keep the new \ healing ear drum in position without moving and also avoids external bacteria from entering the ear.
- There is usually only mild pain following ear surgery. Some discomfort may be felt during one week of pressure dressing which is applied post operatively. Once this is removed, however, most discomfort subsides.
- There may be occasional fleeting, stabbing pain in the ear up to one week after surgery. Analgesics will be prescribed during this time.
- Patients can feel blocked sensation, feeling of bubble popping, water moving in ear following surgery which is due to gel packing of ear canal and middle ear, which slowly subsides once gel foam dissolves in a few weeks post surgery.
- The incision behind the ear should be cleaned twice a day with betadine in order to remove all dried blood after dressing is removed.
- Occasionally, a patient may experience dizziness for a few days after surgery. This occurs due to drilling of infected bone or due to drilling of disease tissue over semicircular canals. Such dizziness usually subsides within several days and is of no serious concern.
- HEARING – Generally, hearing cannot be evaluated for six weeks after surgery. This is because of the fact that the middle ear becomes swollen and fills with blood as a result of the surgical procedure. Also, the entire ear canal is filled with packing material. It takes approximately six weeks for the blood and the packing material to resorb. You may begin to notice occasional popping of the ear several weeks after surgery. This is the result of resorption of the blood and entrance of air into the middle ear cavity. It is a normal part of the healing process.
- Avoid all bending over and lifting heavy objects for at least two weeks after surgery. You should not blow your nose for three weeks. Try to avoid sneezing for the first several weeks post-operatively. If you must sneeze, let it come out of the mouth like a cough. Excessive coughing should also be avoided. You should avoid gym classes or strenuous athletic activity for one month after surgery. Swimming, diving and water skiing should be avoided for two months after surgery.
- Eyeglasses may be worn as soon as the surgical stitches are removed. The hair may be washed with someone’s help. It is essential, however, that the ear canal be kept completely dry. This may be accomplished by placing cotton coated with Vaseline into the ear canal opening.
- The hair may be washed 1 month after surgery, once eardrum and external incision area heals up and only after consulting your surgeon and his confirmation. Place a firm cotton ball in the ear canal and place Vaseline on the outside of the cotton ball while taking bath during second to fourth week.
- RETURNING TO WORK OR SCHOOL – The average patient is usually able to return to school or work one to two weeks following surgery.
- MEDICATIONS – When discharged from the hospital/clinic, you will be given several prescriptions which should be followed.
- Any ear surgery may take 1-3 months to heal completely, during every visit of 7th to 10th day interval, ear will be examined, cleaned and medication suggested according to current ear condition on that day.
- Finally, please follow these instructions faithfully so that you can attain the desired result. If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to call us.
- Tinnitus (ringing sound) which is existing preoperatively will never subside after surgery, it may slightly increase postoperatively as patients hearing becomes better once eardrum completely forms. In Patients developing tinnitus postoperatively it usually subsides in a few months.

Contact us
Bayya Hospitals
12-25-192, Bhagath Singh Centre, Kothapet, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh 522001
0863-2225729
+91 6304429294
+91 93819 22827
Useful Links
Consultation Hours
For ENT
Monday – Saturday 9AM – 1:30 Noon,
Evening 5:30PM to 8:00PM
Sunday – CLOSED
For EYE
Monday – Saturday 9AM – 5:00PM
Sunday – CLOSED