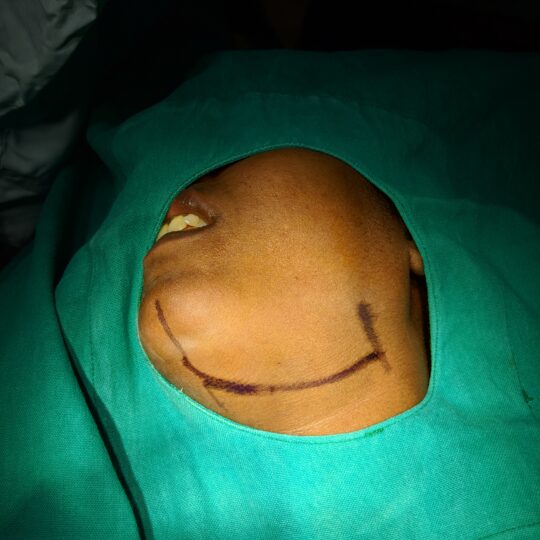
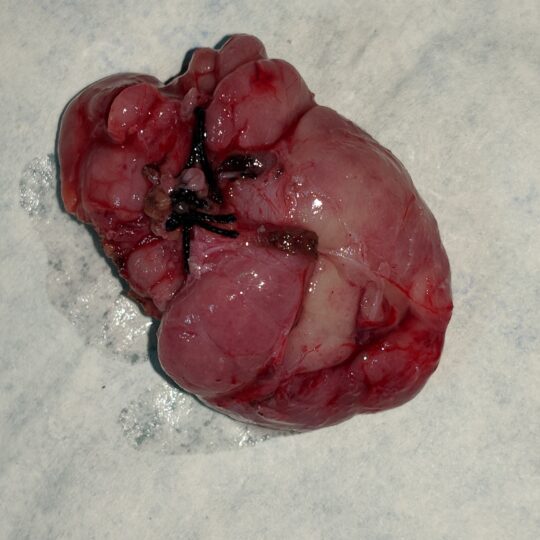
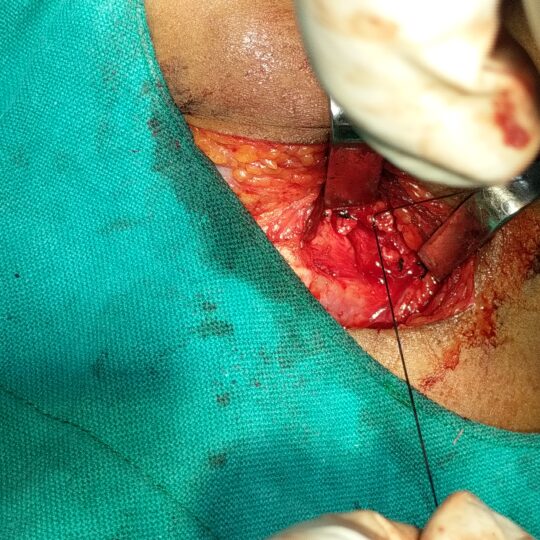
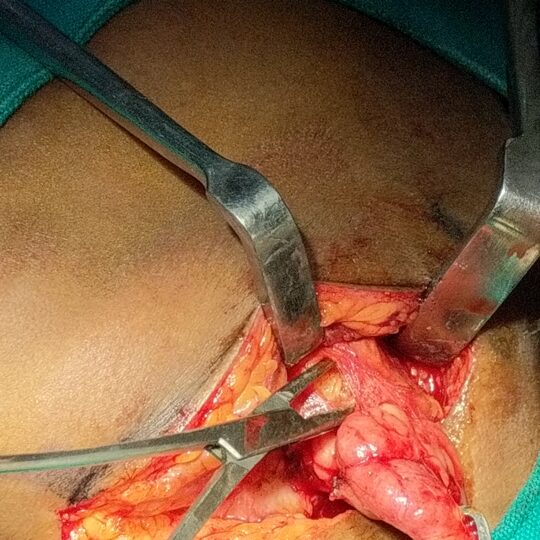
Submandibular Gland
Submandibular gland sialedenitis/sialolithiasis
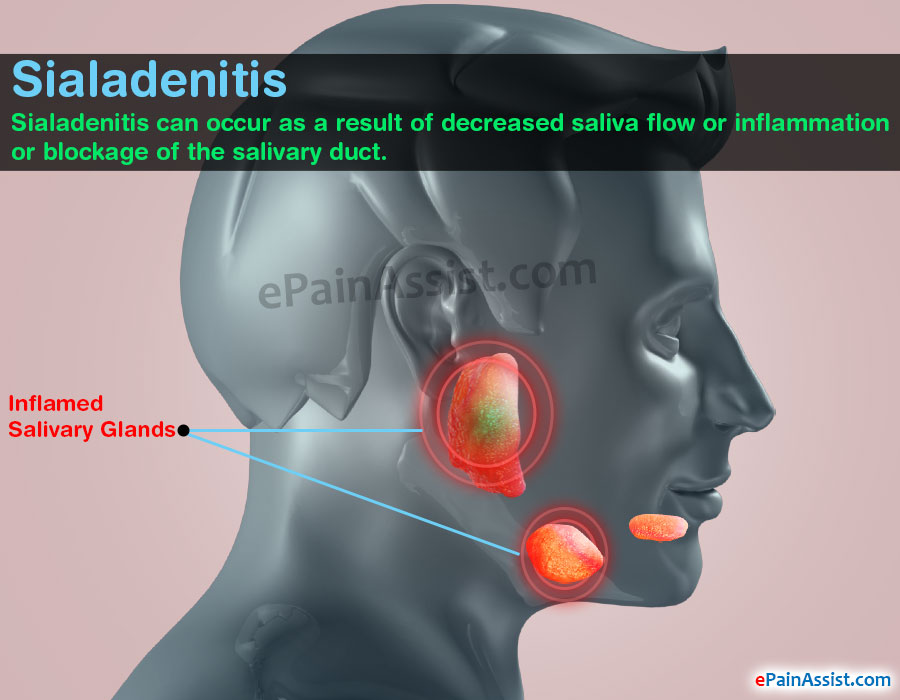
Sialadenitis is bacterial infection of a salivary gland, usually due to an obstructing stone or gland hyposecretion. Symptoms are swelling, pain, redness, and tenderness. Diagnosis is clinical. CT, ultrasonography, and MRI may help identify the cause. Treatment is with antibiotics and painkillers. If the patient is getting recurrent attacks of infection it is better to excise the gland.
What is the submandibular gland?
The submandibular glands are a pair of salivary glands under the jaw bone. Each gland produces saliva which goes through a long duct to its opening under the tongue at the front of the mouth. The production of saliva increases when we eat. The saliva secreted by the submandibular gland is a bit thicker than that produced by other salivary glands. Because of its thickness this saliva can sometimes form little stones.
What problems can you have with the submandibular gland?
The commonest problem is blockage of the salivary duct. This can be caused by the presence of stones or simply a narrowing of the salivary duct. Blockage of the salivary duct can cause a painful swelling of the gland when you eat. Sometimes the swelling may settle on its own. When the blockage is severe, it can lead to persistent inflammation of the gland. Occasionally, a painless lump may develop within the submandibular gland. Those lumps are often benign but need thorough checking, as up to half of them may be or become cancerous. Even benign lumps can get gradually bigger.
What investigation are you likely to have?
An X-ray or CT scan of the submandibular gland to see if there are stones inside the gland or the duct. Sialogram The doctor fills the duct at the front of the mouth with some contrast liquid and then takes x-rays. This will show up stones or narrowing inside the duct. Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to detect any lumps inside the gland. Fine needle aspiration: This can help to find out the nature of the lump. The doctor uses a fine needle to draw some cells out from the lump. The cells are sent to the laboratory for analysis.
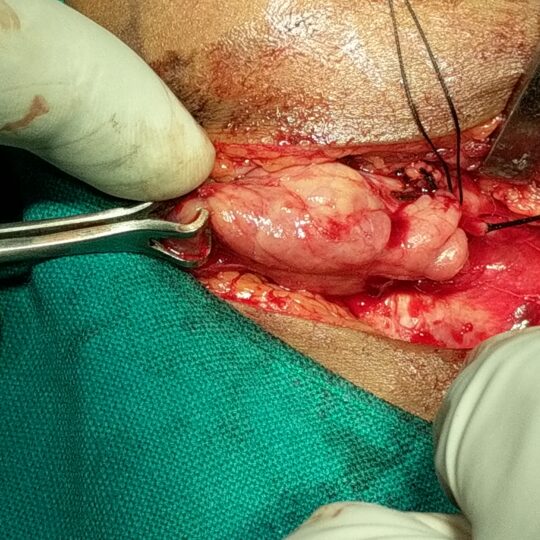
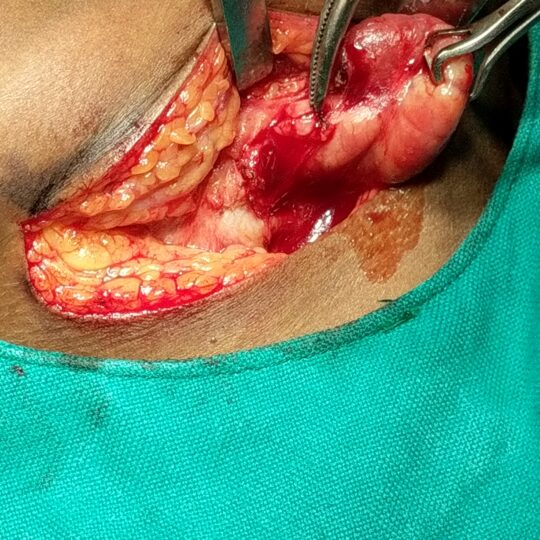
Why operate on the submandibular gland?
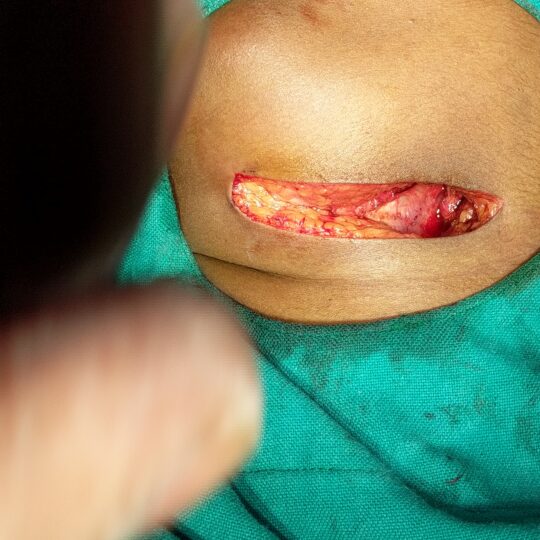
If stones inside the duct do not come out, the gland may swell up when you eat and get infected repeatedly.. Second indication of surgery is in tumours of submandibular gland.
- Date of admission will be discussed with patient
- Do not eat or drink anything for 6 hours before the operation.
- Your doctor must know what medicines you take, especially medicines which affect blood clotting.
- Take medicines suggested by us night before surgery.
- You will be asleep for the operation and is done under anaesthesia.
- The operation usually takes about 1 hour.
- During the operation care will be taken to try and avoid damage to 3 important nerves in the vicinity of the submandibular gland.
- After the operation you will wake up in the recovery room.
- When you are stable you will return to your regular hospital bed.
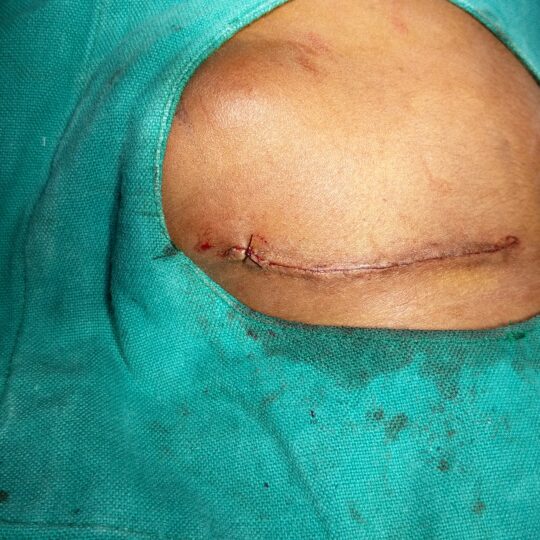
- There may be a drain at the site of the incision.
- We will discuss with you when you may be discharged.
- Pain is usually not severe and is easily controlled.
- As this is a delicate operation you need to be aware of possible complications.
- An attempt will be made to avoid damaging the nerve supplying the lower lip. Damage to this nerve does occasionally occur. This results in an abnormality of lip appearance and movement. This paralysis is sometimes temporary.
- Important nerves supplying the taste sensation and movement of the tongue lie deep to the gland. It is very rare for these to be damaged, but it is possible.
- A haematoma in the wound is rare.
- An infection in the wound is possible.
- The wound usually heals well.
- Injury to the deeper structures of the neck is very rare.

Contact us
Bayya Hospitals
12-25-192, Bhagath Singh Centre, Kothapet, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh 522001
0863-2225729
+91 6304429294
+91 93819 22827
Useful Links
Consultation Hours
For ENT
Monday – Saturday 9AM – 1:30 Noon,
Evening 5:30PM to 8:00PM
Sunday – CLOSED
For EYE
Monday – Saturday 9AM – 5:00PM
Sunday – CLOSED